Heat Treatment Process in Coimbatore
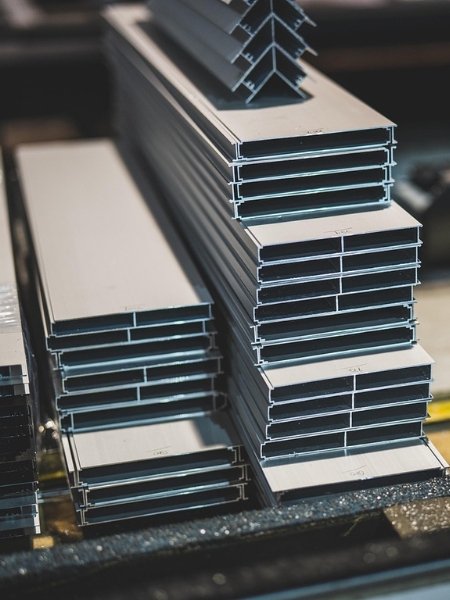
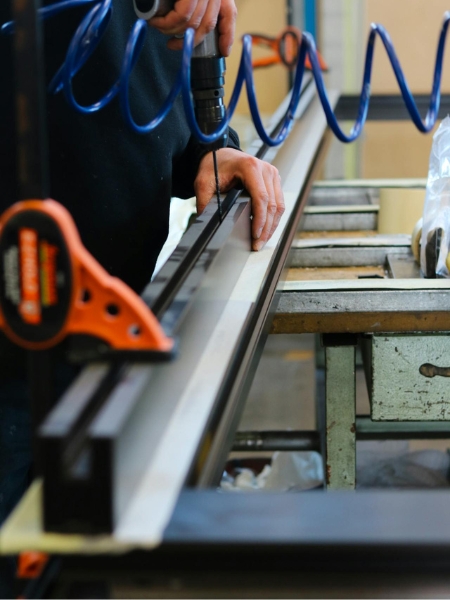
The heat treatment of aluminum is a controlled heat treatment process used to enhance its mechanical properties, such as strength, hardness, and ductility. This involves a structured heat treatment procedure, including solution heat treatment, quenching, and aging, which modify the material’s microstructure for improved performance in aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications. Unlike ferrous metals, aluminum does not undergo normalizing heat treatment, as normalization is primarily used to refine grain structure and relieve stresses in steels. However, we are one of the leading heat treatment process in Coimbatore & alternative treatments like annealing and stress relieving are used to achieve similar effects in aluminum alloys.
Types of heat treatment processes:
Solution Heat Treatment (Solutionizing):
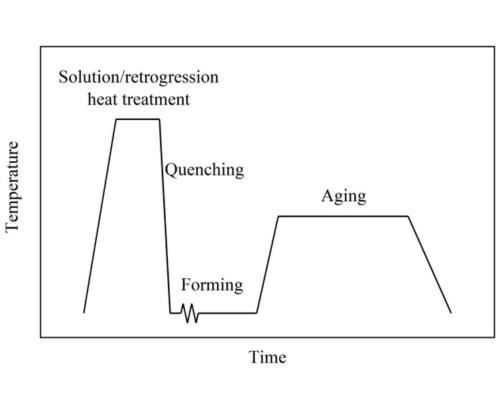
Solution Heat Treatment (Solutionizing) is a crucial heat treatment process for aluminum alloys, where the material is heated to a high temperature (typically 450-550°C) to dissolve alloying elements into the aluminum matrix. This process enhances the alloy’s mechanical properties by creating a uniform microstructure. After maintaining the temperature for a specific duration, the aluminum is rapidly quenched in water or another cooling medium to lock the dissolved elements in place, forming a supersaturated solid solution. This prepares the alloy for subsequent aging (natural or artificial), which further strengthens the material. Solution heat treatment is widely used for heat-treatable aluminum alloys, such as 2xxx, 6xxx, and 7xxx series, in industries like aerospace, automotive, and construction.
Quenching:
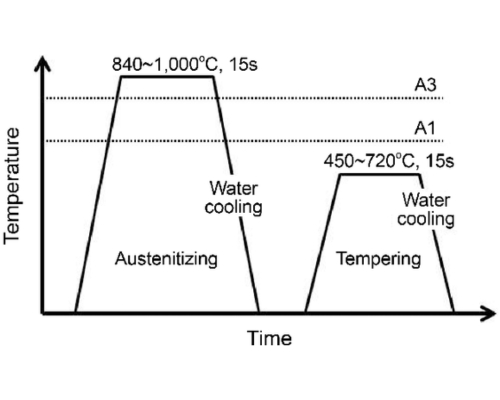
Quenching is a vital step in the heat treatment process for aluminum, where the material is rapidly cooled using water, oil, or air after being heated during solution heat treatment. This rapid cooling is essential in the hardening process, as it locks the alloying elements in a supersaturated state, enhancing strength and durability. Unlike ferrous metals, aluminum does not undergo induction hardening, case hardening process, or surface hardening process, as these are typically used for steels to improve wear resistance. However, quenching in the heat treatment process prepares aluminum alloys for subsequent aging treatments, which further improve their mechanical properties for applications in aerospace, automotive, and industrial sectors.
Hardening:
Hardening of aluminum is achieved through a specialized hardening process that involves solution heat treatment, quenching, and aging to enhance strength and durability. Unlike steels, aluminum does not undergo induction hardening, case hardening process, or surface hardening process, as these methods are typically used to improve surface wear resistance in ferrous metals. Instead, aluminum alloys rely on the heat treatment process, where they are heated to dissolve alloying elements, rapidly quenched to retain a supersaturated structure, and then aged to develop maximum hardness. This heat treatment process is essential in industries like aerospace, automotive, and construction, where lightweight yet strong materials are required.
Annealing:
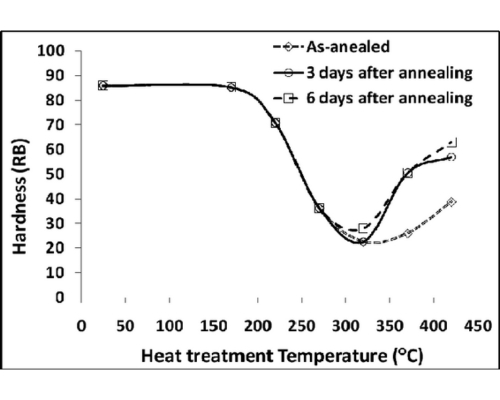
Annealing is a heat treatment process in metallurgy that involves heating aluminum to a specific temperature and then cooling it to enhance its ductility and reduce hardness, making it more workable. This process, known as process annealing, is commonly used to relieve internal stresses and improve machinability. Induction annealing, a method where heat is generated by electromagnetic induction, is often employed for localized heating of aluminum components, allowing for precise control over the heat treatment process. By carefully controlling the temperature and cooling rate during annealing, manufacturers can achieve desired mechanical properties in aluminum alloys, ensuring they meet specific performance requirements. The heat treatment process, including annealing, plays a crucial role in determining the final characteristics of aluminum products used in various applications.
Stress Relieving:

Stress relieving is a heat treatment process designed to reduce internal stresses in metals that have been subjected to manufacturing processes such as welding, machining, or forming. By heating the material to a specific temperature below its critical transformation point and holding it for a predetermined period, internal stresses are redistributed without altering the material's mechanical properties or causing phase transformations. This controlled heating and cooling process enhances dimensional stability and reduces the risk of distortion or cracking during subsequent operations.





